Section 2
Body Fluids
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
4 concepts
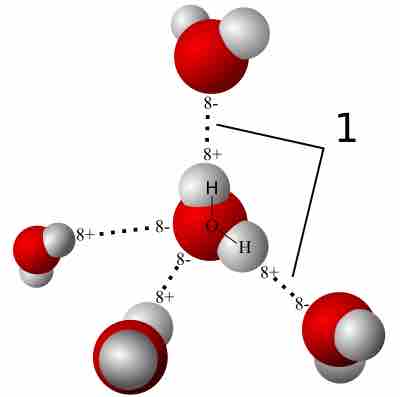
Water Content in the Body
A significant percentage of the human body is water, which includes intracellular and extracellular fluids.
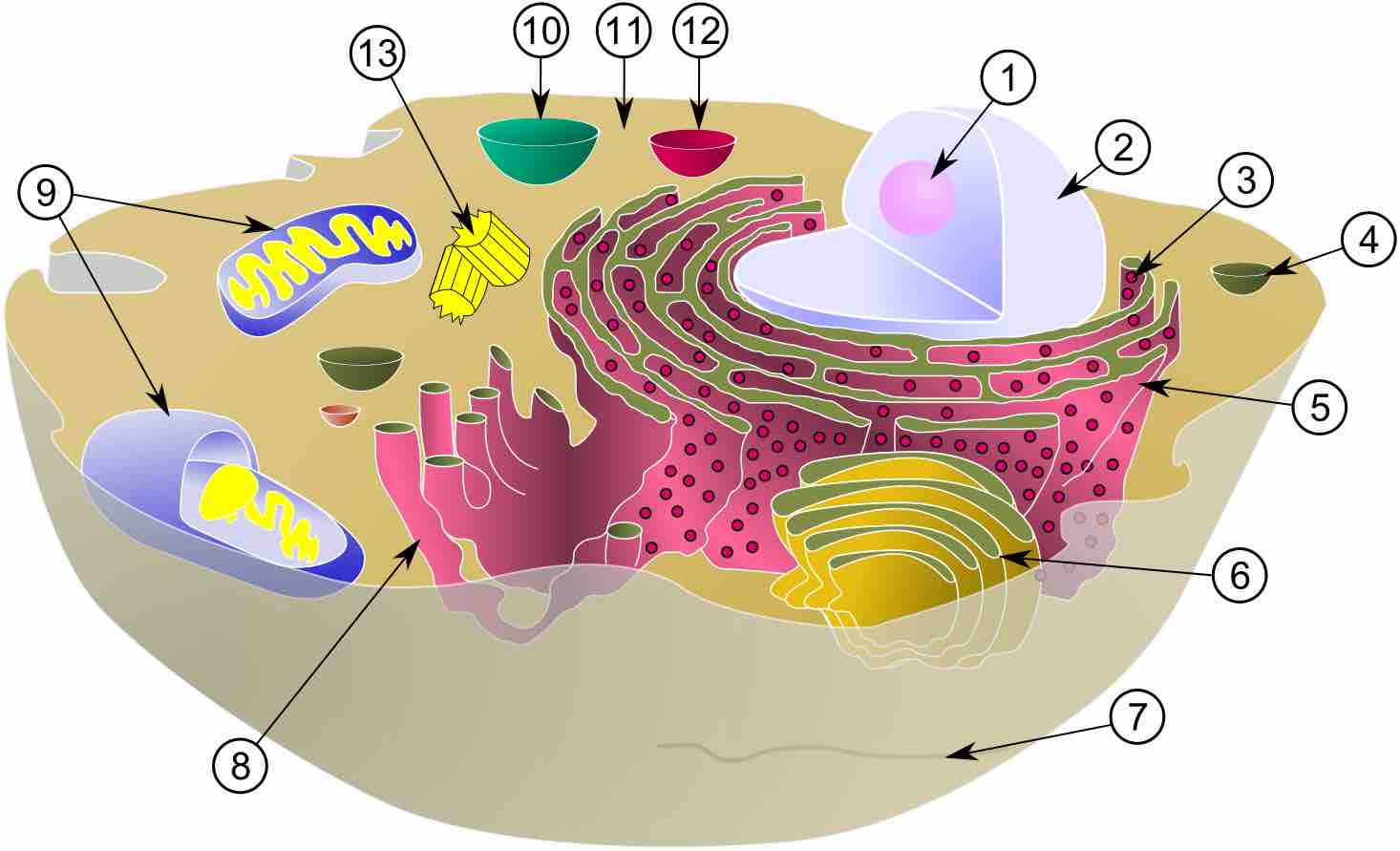
Fluid Compartments
The major body fluid compartments include: intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid (plasma, interstitial fluid, and trancellular fluid).
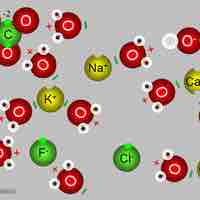
Body Fluid Composition
The composition of tissue fluid depends upon the exchanges between the cells in the biological tissue and the blood.
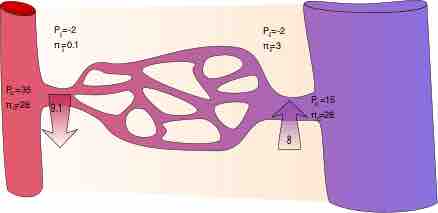
Movement of Fluid Among Compartments
Movement of fluid among compartments depends on several variables described by Starling's equation.