Section 3
Periodic Motion
By Boundless
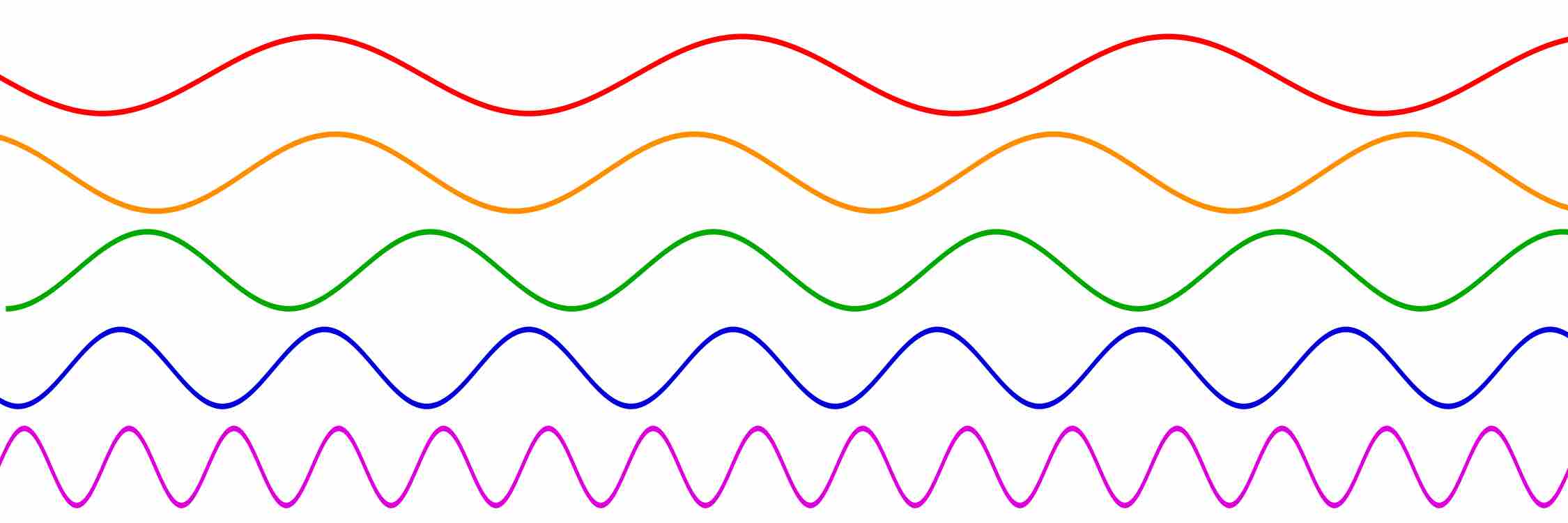
The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, while the frequency is the number of cycles per unit time.
The period of a mass m on a spring of spring constant k can be calculated as
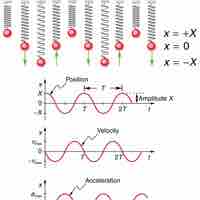
Simple harmonic motion is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement.
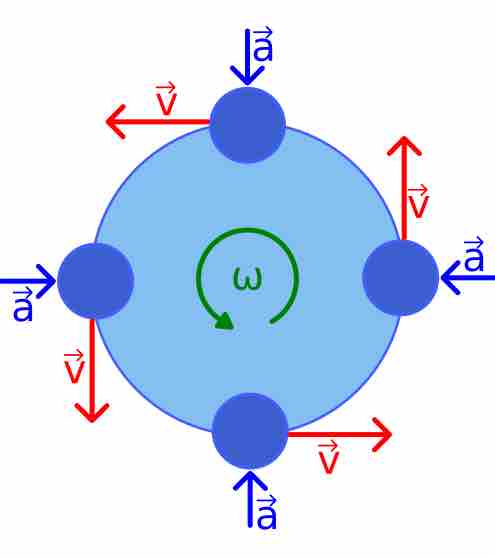
Simple harmonic motion is produced by the projection of uniform circular motion onto one of the axes in the x-y plane.
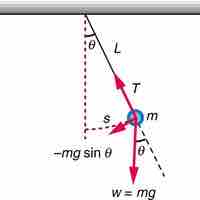
A simple pendulum acts like a harmonic oscillator with a period dependent only on L and g for sufficiently small amplitudes.
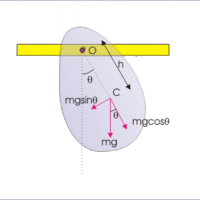
The period of a physical pendulum depends upon its moment of inertia about its pivot point and the distance from its center of mass.
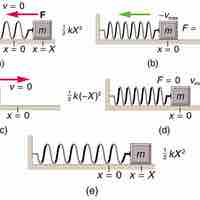
The total energy in a simple harmonic oscillator is the constant sum of the potential and kinetic energies.
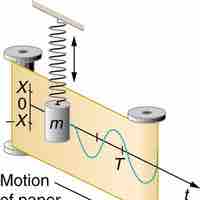
The solutions to the equations of motion of simple harmonic oscillators are always sinusoidal, i.e., sines and cosines.