Section 6
Kepler's Laws
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
5 concepts
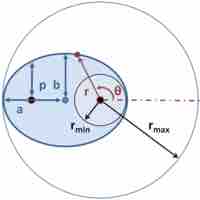
Kepler's First Law
Kepler's first law is: The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci.
Kepler's Second Law
Kepler's second law states: A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.
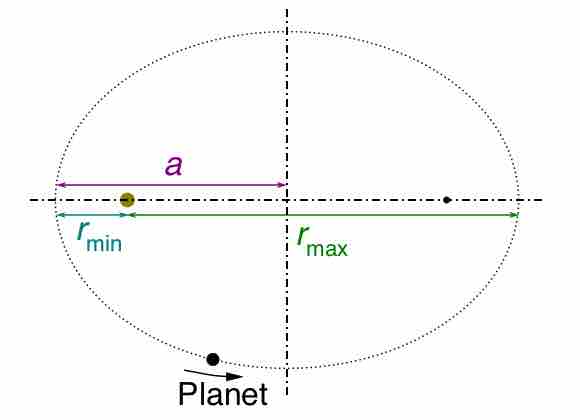
Kepler's Third Law
Kepler's third law states that the square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit.

Orbital Maneuvers
An orbital maneuver is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft (the rest of the flight is called "coasting").

Satellites
Natural satellites are celestial objects that orbit a larger body; artificial satellites are manmade objects put in the orbit of the Earth.