Section 3
Projectile Motion
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
5 concepts
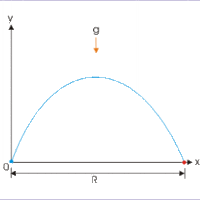
Basic Equations and Parabolic Path
Projectile motion is a form of motion where an object moves in parabolic path; the path that the object follows is called its trajectory.
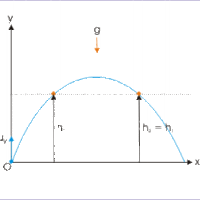
Solving Problems
In projectile motion, an object moves in parabolic path; the path the object follows is called its trajectory.
Zero Launch Angle
An object launched horizontally at a height
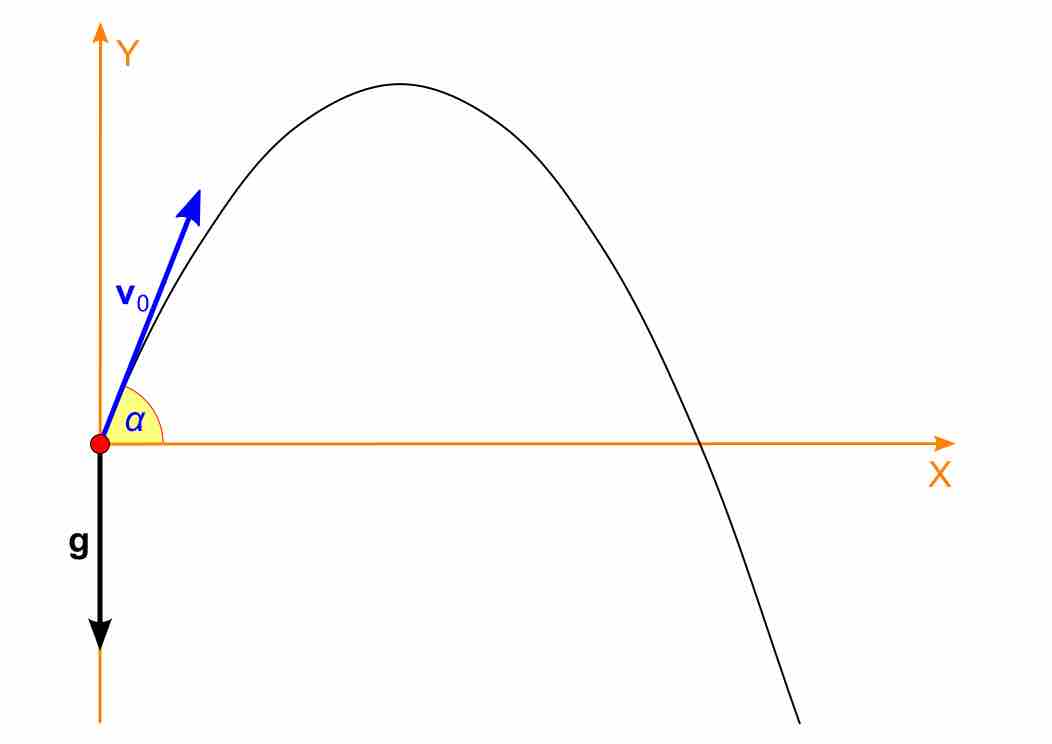
General Launch Angle
The initial launch angle (0-90 degrees) of an object in projectile motion dictates the range, height, and time of flight of that object.
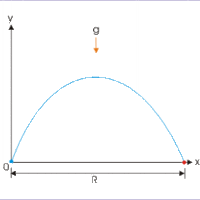
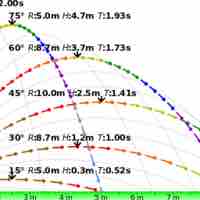
Key Points: Range, Symmetry, Maximum Height
Projectile motion is a form of motion where an object moves in parabolic path. The path that the object follows is called its trajectory.