Section 5
Kinetic Theory
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
4 concepts
Origin of Pressure
Pressure is explained by kinetic theory as arising from the force exerted by molecules or atoms impacting on the walls of a container.
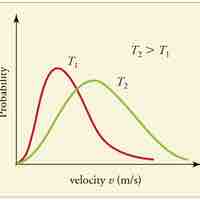
Speed Distribution of Molecules
A gas of many molecules has a predictable distribution of molecular speeds, known as the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Temperature
Temperature is directly proportional to the average translational kinetic energy of molecules in an ideal gas.

Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas
Internal energy is the total energy contained by a thermodynamic system, and has two major components: kinetic energy and potential energy.