Section 2
Radioactivity
By Boundless
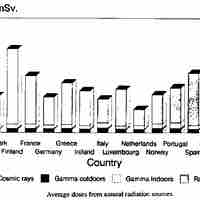
Detectable amounts of radioactive material occurs naturally in soil, rocks, water, air, and vegetation.
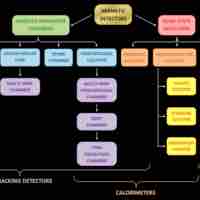
A radiation detector is a device used to detect, track, or identify high-energy particles.
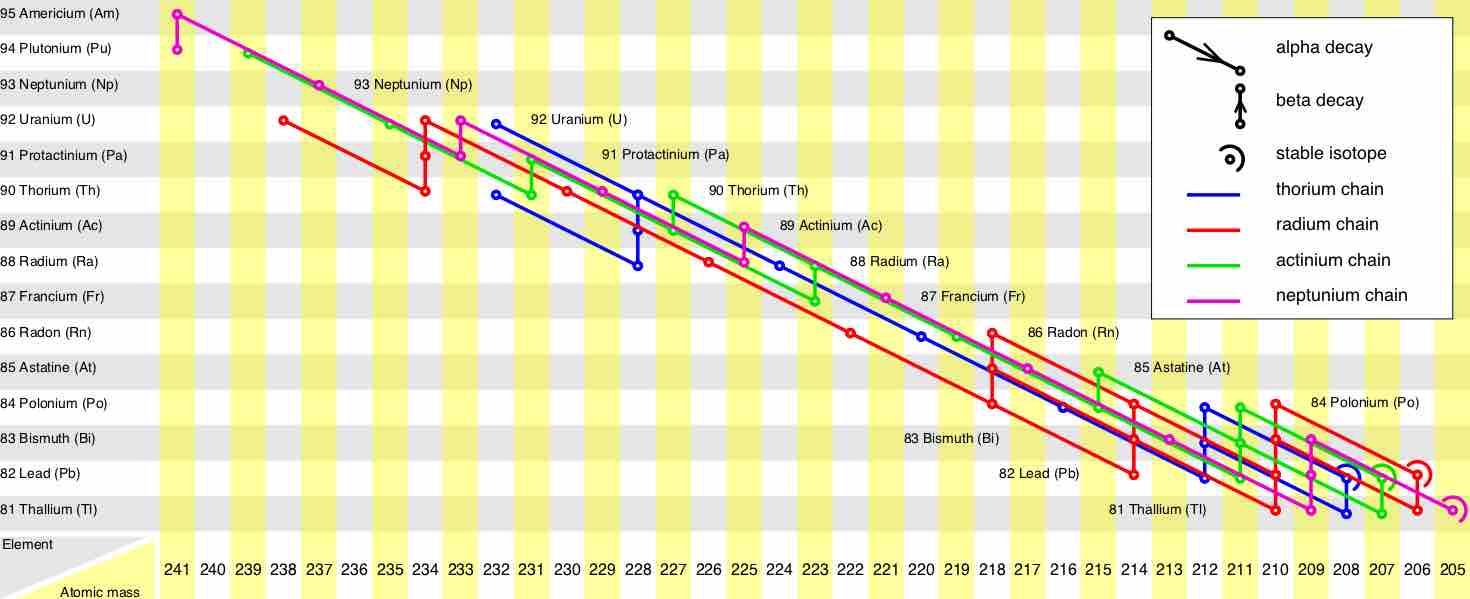
Radioactive decay series describe the decay of different discrete radioactive decay products as a chained series of transformations.
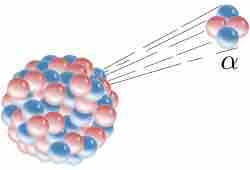
In alpha decay an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and transforms into an atom with smaller mass (by four) and atomic number (by two).
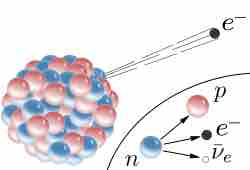
Beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (an electron or a positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus.
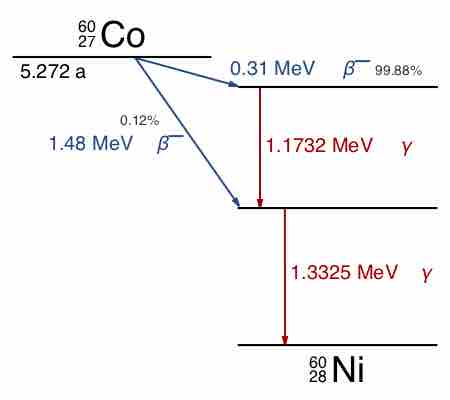
Gamma decay is a process of emission of gamma rays that accompanies other forms of radioactive decay, such as alpha and beta decay.
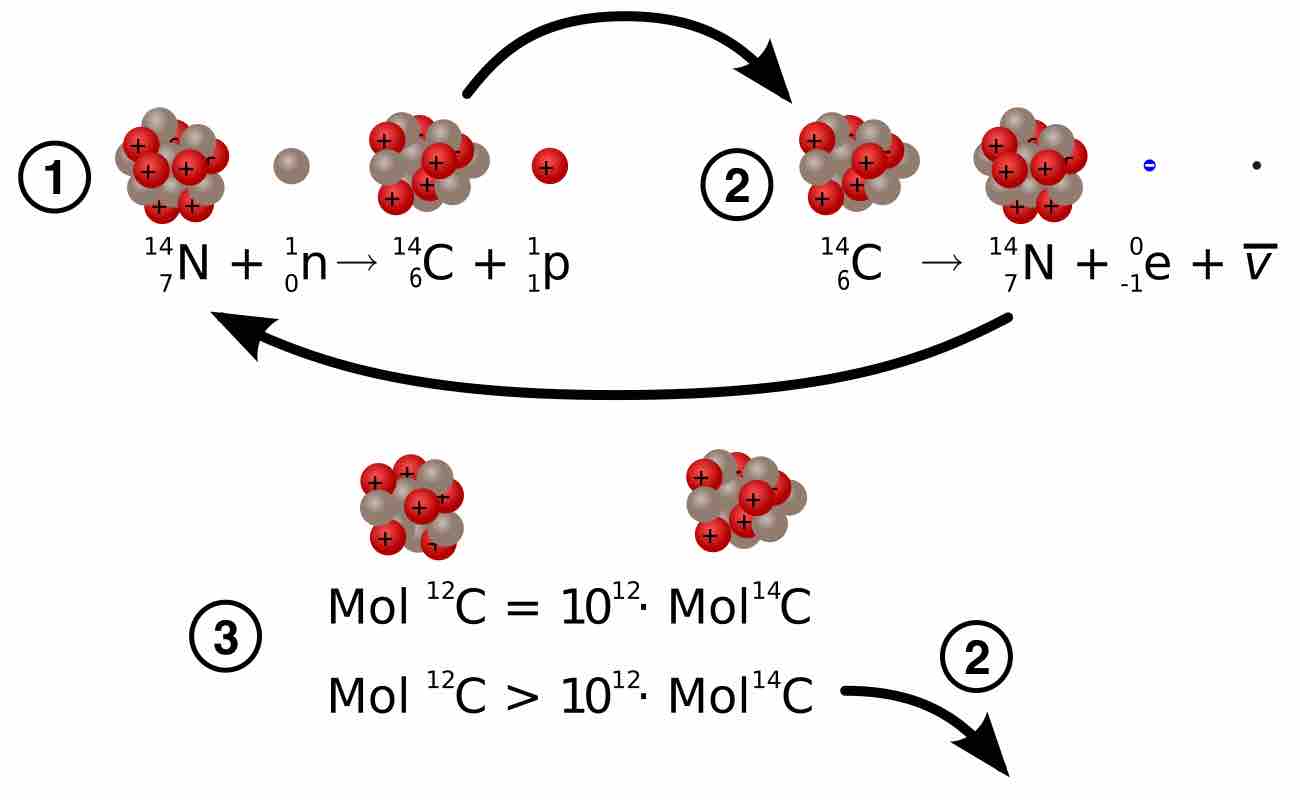
Carbon-14 dating is a radiometric dating method that uses the radioisotope carbon-14 (14C) to estimate the age of object.

The half-life of a radionuclide is the time taken for half the radionuclide's atoms to decay.