Section 3
Collisions
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
6 concepts
Conservation of Energy and Momentum
In an inelastic collision the total kinetic energy after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision.
Glancing Collisions
Glancing collision is a collision that takes place under a small angle, with the incident body being nearly parallel to the surface.

Elastic Collisions in One Dimension
An elastic collision is a collision between two or more bodies in which kinetic energy is conserved.
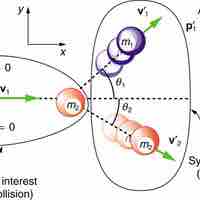
Elastic Collisions in Multiple Dimensions
To solve a two dimensional elastic collision problem, decompose the velocity components of the masses along perpendicular axes.

Inelastic Collisions in One Dimension
Collisions may be classified as either inelastic or elastic collisions based on how energy is conserved in the collision.
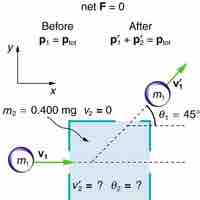
Inelastic Collisions in Multiple Dimensions
While inelastic collisions may not conserve total kinetic energy, they do conserve total momentum.