Section 2
Density and Pressure
By Boundless
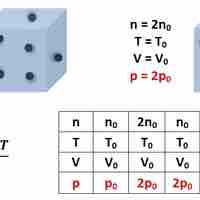
Pressure is scalar quantity which is defined as force per unit area where the force acts in a direction perpendicular to the surface.
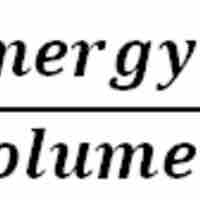
Pressure within static fluids depends on the properties of the fluid, the acceleration due to gravity, and the depth within the fluid.
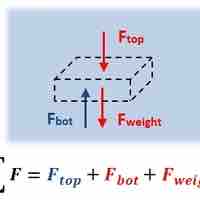
Any region or point, or any static object within a static fluid is in static equilibrium where all forces and torques are equal to zero.
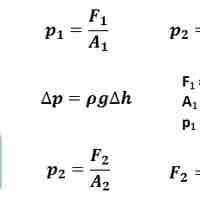
Pascal's Principle states that pressure is transmitted and undiminished in a closed static fluid.
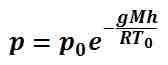
Pressure is often measured as gauge pressure, which is defined as the absolute pressure minus the atmospheric pressure.
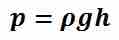
Barometers are devices used for measuring atmospheric and gauge pressure indirectly through the use of hydrostatic fluids.
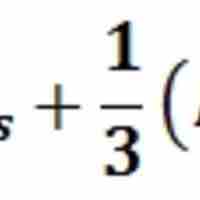
Pressure plays an essential role in a number of critical bodily functions including respiration and blood circulation.