Section 1
Overview
By Boundless
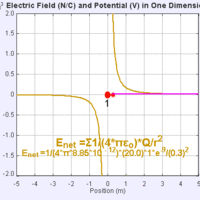
Electric potential and field are related in that potential is a property of the field that describes the field's action.
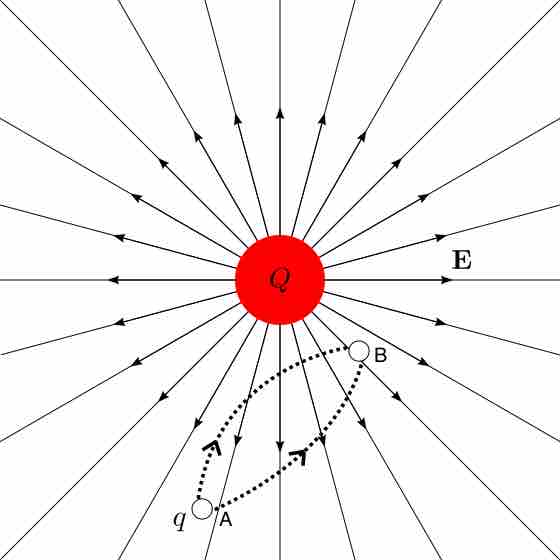
Electric potential energy results from forces between charges; potential difference is the energy needed to move a charge from point A to B.
Electric field is the gradient of potential, which depends inversely upon distance of a given point of interest from a charge.
Electric potential within a charged conductor is equal to zero, but can be calculated as a nonzero value outside of a charged conductor.
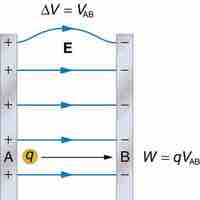
An electric field that is uniform is one that reaches the unattainable consistency of being constant throughout.
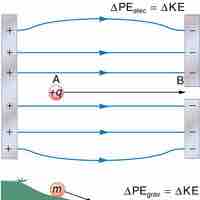
Energy is conserved in the movement of a charged particle through an electric field, as it is in every other physical situation.

The electron volt is a unit of energy useful in the physics of elementary charges and electricity.
The electric dipole moment is a measure of polarity in a system.