Section 12
Tools of Genetic Engineering
By Boundless
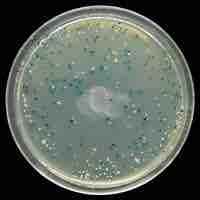
Molecular cloning permits the replication of a specific DNA sequence in a living microorganism.
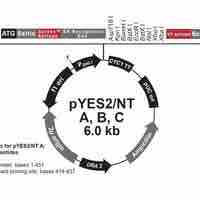
A selectable marker is usually a gene that confers resistance to an antibiotic that would otherwise kill the cells.
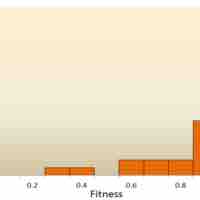
Mutations are accidental changes in a genomic sequence of DNA; this includes the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence.
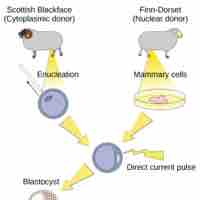
Reproductive cloning, possible through artificially-induced asexual reproduction, is a method used to make a clone of an entire organism.
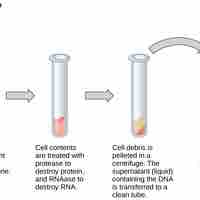
Basic techniques used in genetic material manipulation include extraction, gel electrophoresis, PCR, and blotting methods.
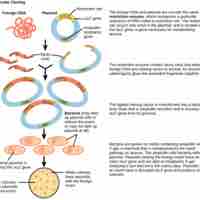
Molecular cloning reproduces the desired regions or fragments of a genome, enabling the manipulation and study of genes.
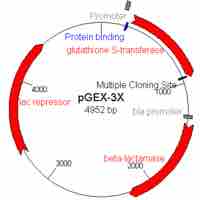
Plasmids can be used as cloning vectors, allowing the insertion of exogenous DNA into a bacterial target.