Section 14
Cloning Techniques
Book
Version 6
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Microbiology
Microbiology
by Boundless
6 concepts
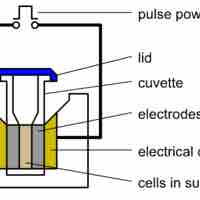
Putting Foreign DNA into Cells
The methods used to get DNA into cells are varied (e.g., transformation, transduction, transfection, and electroporation).
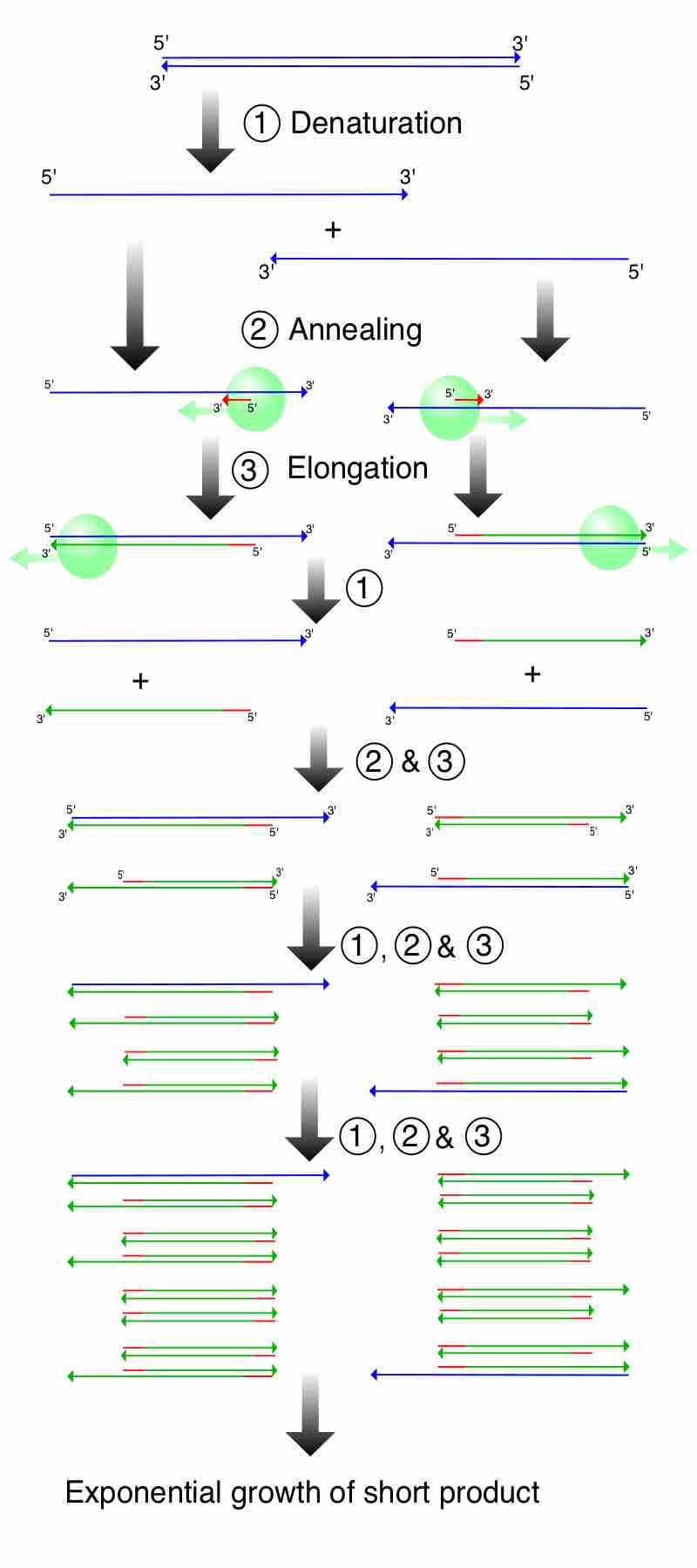
Obtaining DNA
When cloning genomic DNA, the DNA to be cloned is extracted from the organism of interest.
Hosts for Cloning Vectors
The majority of molecular cloning experiments begin with a laboratory strain of the bacterium E. coli (Escherichia coli) as the host.

Shuttle Vectors and Expression Vectors
An expression vector is generally a plasmid that is used to introduce a specific gene into a target cell.
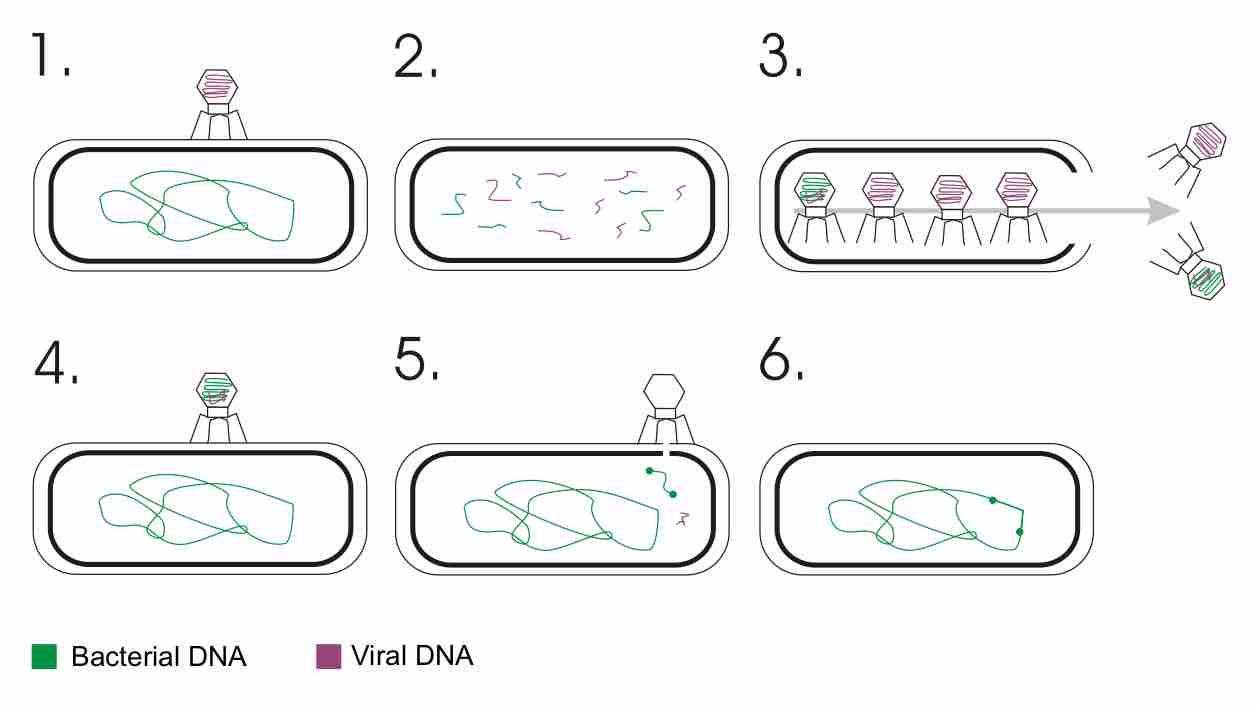
Bacteriophage Lambda as a Cloning Vector
Enterobacteria phage λ (lambda phage, coliphage λ) is a bacterial virus that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli.
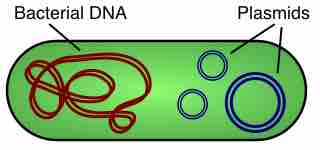
Vectors for Genomic Cloning and Sequencing
In molecular biology, a vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to transfer foreign genetic material into another cell.