Section 17
Fungi
By Boundless

Fungi, latin for mushroom, are eukaryotes which are responsible for decomposition and nutrient cycling through the environment.

From crop and food spoilage to severe infections in animal species, fungal parasites and pathogens are wide spread and difficult to treat.

Fungi are the major decomposers of nature; they break down organic matter which would otherwise not be recycled.
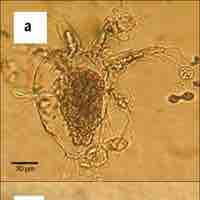
Chytrids are the most primitive group of fungi and the only group that possess gametes with flagella.

Zygomycota, a small group in the fungi kingdom, can reproduce asexually or sexually, in a process called conjugation.
Glomeromycetes are an important group of fungi that live in close symbiotic association with the roots of trees and plants.
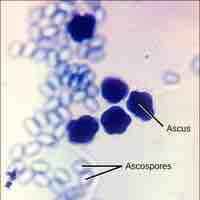
Most fungi belong to the Phylum Ascomycota, which uniquely forms of an ascus, a sac-like structure that contains haploid ascospores.

The basidiomycota are mushroom-producing fungi with developing, club-shaped fruiting bodies called basidia on the gills under its cap.