Section 4
Basic Economic Questions
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Economics
Economics
by Boundless
5 concepts
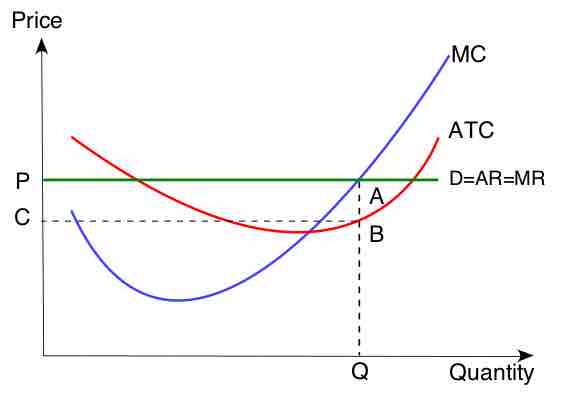
Production Outputs
A firm's production outputs are what it creates using its resources: goods or services.

Production Inputs and Process
Labor, capital, and land are the three necessary inputs for any production process.
Production Recipients
The process of producing and distributing a good or service is called a supply chain, and it is composed of many economic actors.

Differences Between Centrally Planned and Market Economies
The key difference between centrally planned and market economies is the degree of individual autonomy.
Mixed Economies
A mixed economy is a system that embraces elements of centrally planned and free market systems.