Section 2
Barriers to Entry: Reasons for Monopolies to Exist
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Economics
Economics
by Boundless
6 concepts

Resource Control
Control over a natural resource that is critical to the production of a final good is one source of monopoly power.

Economies of Scale and Network Externalities
Economies of scale and network externalities discourage potential competitors from entering a market.

Government Action
There are two types of government-initiated monopoly: a government monopoly and a government-granted monopoly.

Legal Barriers
The government creates legal barriers through patents, copyrights, and granting exclusive rights to companies.
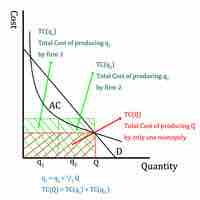
Natural Monopolies
Natural monopolies occur when a single firm can serve the entire market at a lower cost than a combination of two or more firms.

Other Barriers to Entry
Firms gain monopolistic power as a result of markets' barriers to entry, which discourage potential competitors.