Section 5
Functional Group Names, Properties, and Reactions
By Boundless
Functional groups refer to specific atoms bonded in a certain arrangement that give a compound certain physical and chemical properties.
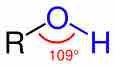
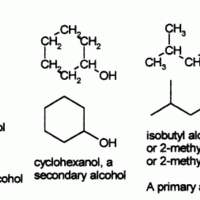
Alcohols are functional groups characterized by the presence of an -OH group.

Ethers are a class of organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups.
Aldehydes and ketones are classes of organic compounds that contain a carbonyl (C=O) group.
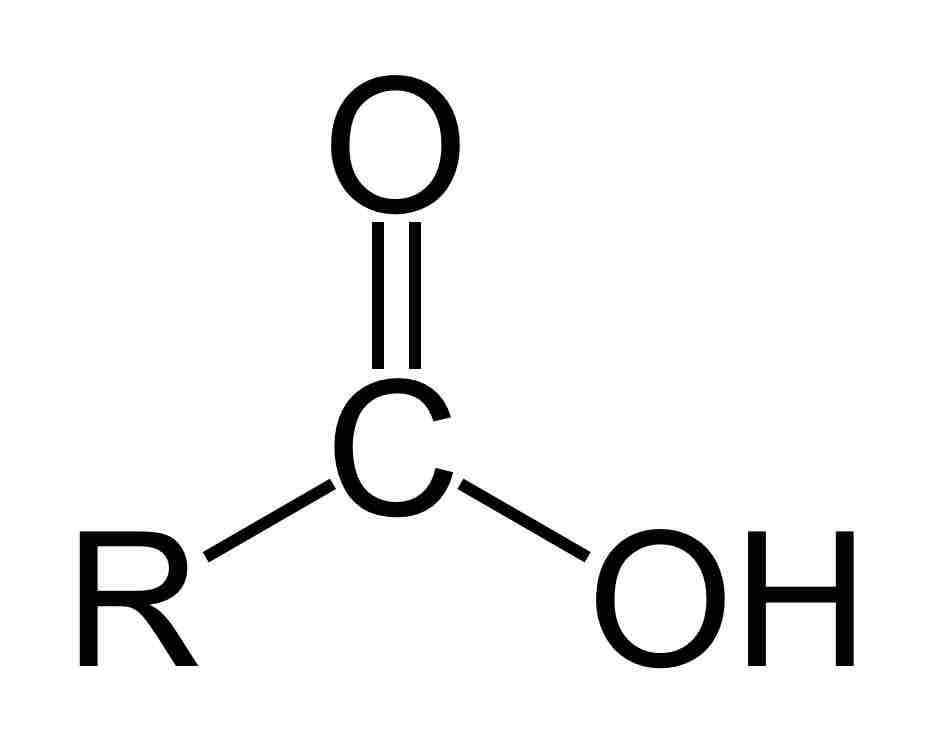
Carboxylic acids are organic acids that contain a carbon atom that participates in both a hydroxyl and a carbonyl functional group.
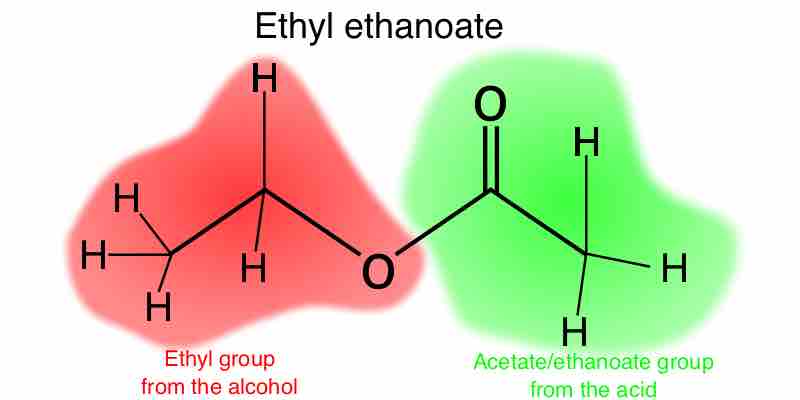
Esters are functional groups produced from the condensation of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid, and are named based on these components.
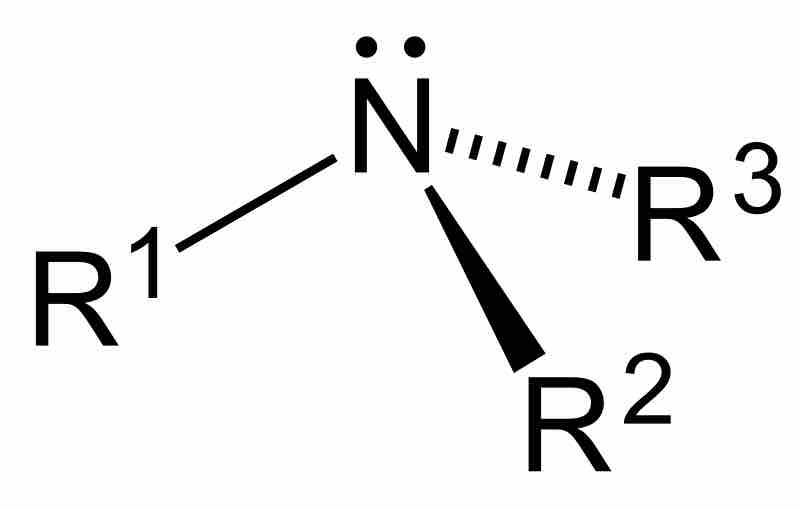
Amines are compounds characterized by the presence of a nitrogen atom, a lone pair of electrons, and three substituents.