Section 2
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
4 concepts
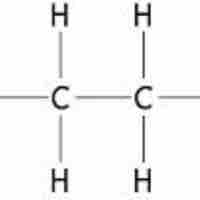
Alkanes
Alkanes are relatively unreactive hydrocarbons that contain no double or triple bonds in their carbon skeletons.

Reactions of Alkanes
Alkanes are generally unreactive, but can participate in oxidation, halogenation, and cracking reactions.
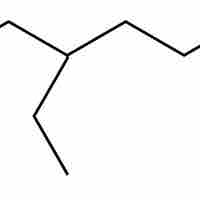
Drawing Hydrocarbon Structures
Hydrocarbon structures can be drawn from the IUPAC names of chemical compounds by starting with the carbon backbone and adding substituents.
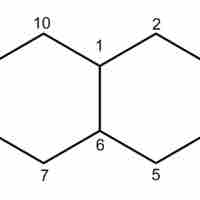
Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain a ring in their carbon backbones.