Section 6
Electrolysis
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
4 concepts
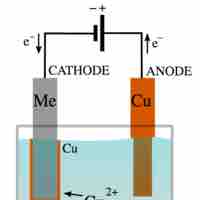
Predicting the Products of Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a way of separating a compound by passing an electric current through it; the products are the compound's component ions.
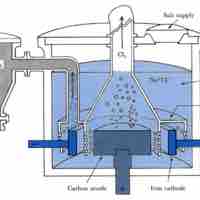
Electrolysis of Sodium Chloride
Two commonly used methods of electrolysis involve molten sodium chloride and aqueous sodium chloride, which give different products.
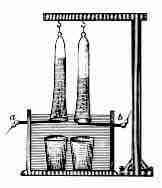
Electrolysis of Water
Pure water cannot undergo significant electrolysis without an electrolyte, such as an acid or a base.
Electrolysis Stoichiometry
The amount of chemical change that occurs in electrolysis is stoichiometrically related to the amount of electrons that pass through the cell.