Section 3
Activation Energy and Temperature Dependence
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
4 concepts
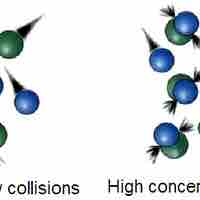
The Collision Theory
Collision theory provides a qualitative explanation of chemical reactions and the rates at which they occur, appealing to the principle that molecules must collide to react.
Factors that Affect Reaction Rate
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on factors that affect whether reactants can collide with sufficient energy for reaction to occur.

The Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation is a formula that describes the temperature-dependence of a reaction rate.
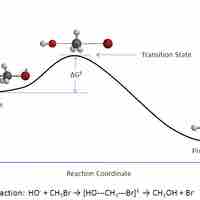
Transition State Theory
In a given chemical reaction, the hypothetical space that occurs between the reactants and the products is known as the transition state.