Section 1
Acids and Bases
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
6 concepts

Nature of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases will neutralize one another to form liquid water and a salt.
The Arrhenius Definition
An Arrhenius acid dissociates in water to form hydrogen ions, while an Arrhenius base dissociates in water to form hydroxide ions.
The Brønsted-Lowry Definition of Acids and Bases
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any species capable of donating a proton; a Brønsted-Lowry base is any species capable of accepting a proton.
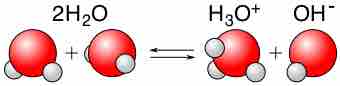
Acid-Base Properties of Water
Water is capable of acting as either an acid or a base and can undergo self-ionization.
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is the measure of the strength of an acid in solution.
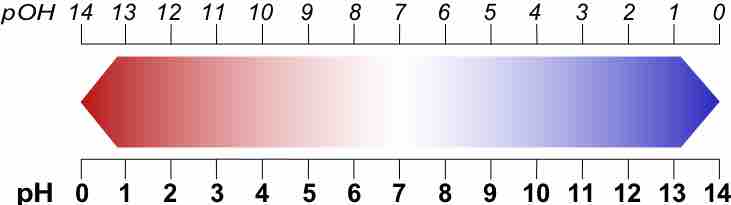
pOH and Other p Scales
A p-scale is a negative logarithmic scale.