Section 7
The Evolution of Primates
Book
Version 32
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Biology
Biology
by Boundless
4 concepts
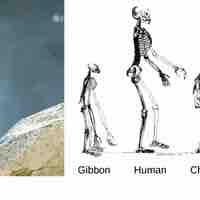
Characteristics and Evolution of Primates
All primates exhibit adaptations for climbing trees and have evolved into two main groups: Prosimians and Anthropoids.
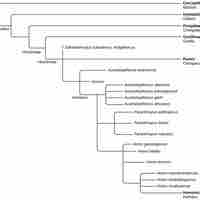
Early Human Evolution
Modern humans and chimpanzees evolved from a common hominoid ancestor that diverged approximately 6 million years ago.
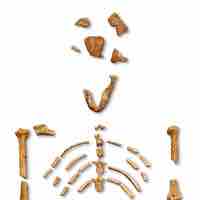
Early Hominins
The hominin Australopithecus evolved 4 million years ago and is believed to be in the ancestral line of the genus Homo.

Genus Homo
The human genus Homo, which includes modern humans as well as extinct human relatives, appeared around 2.3 million years ago.