Section 3
Laws of Inheritance
By Boundless
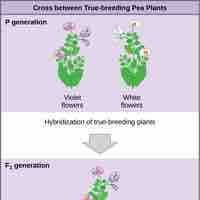
Mendel formed the Laws of Heredity (the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment) from his pea plant experiments.

In a heterozygote, the allele which masks the other is referred to as dominant, while the allele that is masked is referred to as recessive.
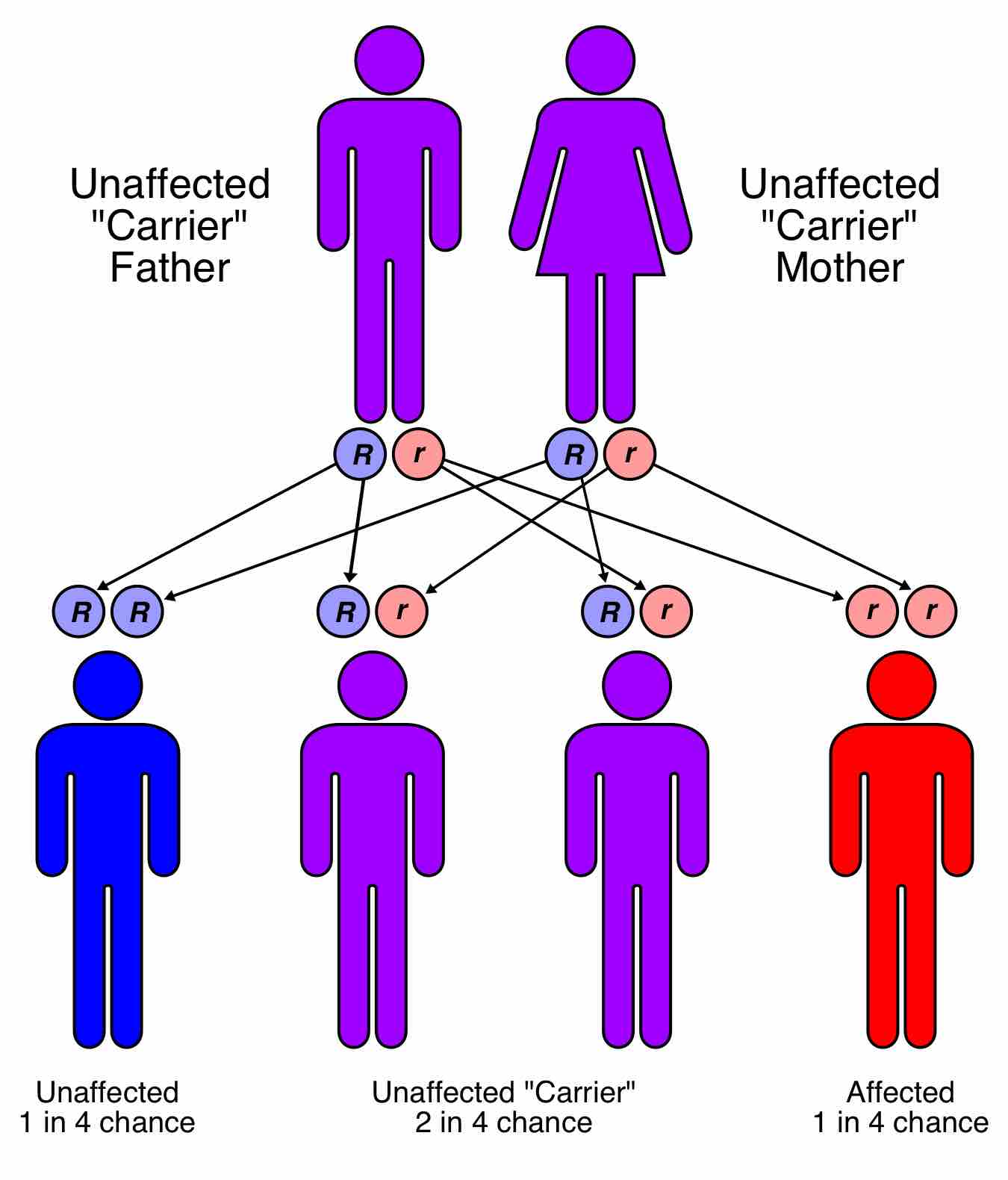
Mendel's Law of Segregation states that a diploid organism passes a randomly selected allele for a trait to its offspring, such that the offspring receives one allele from each parent.
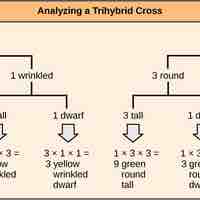
Independent assortment allows the calculation of genotypic and phenotypic ratios based on the probability of individual gene combinations.
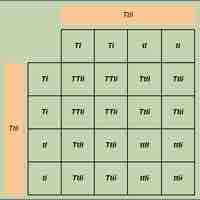
Genes that are on the same chromosome, or "linked", do not assort independently, but can be separated by recombination.
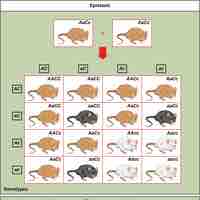
Epistasis occurs when one gene masks or interferes with the expression of another.