Section 2
Prokaryotic Transcription
Book
Version 32
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Biology
Biology
by Boundless
3 concepts
Transcription in Prokaryotes
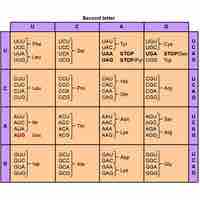
The genetic code is a degenerate, non-overlapping set of 64 codons that encodes for 21 amino acids and 3 stop codons.
Initiation of Transcription in Prokaryotes
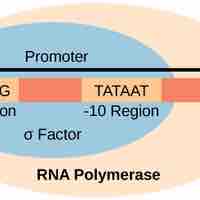
RNA polymerase initiates transcription at specific DNA sequences called promoters.
Elongation and Termination in Prokaryotes
Transcription elongation begins with the release of the polymerase σ subunit and terminates via the rho protein or via a stable hairpin.