Section 1
Signaling Molecules and Cellular Receptors
Book
Version 32
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Biology
Biology
by Boundless
4 concepts

Signaling Molecules and Cellular Receptors
Cellular communication ensures regulation of biological processes within various environments from single-celled to multicellular organisms.
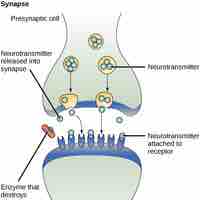
Forms of Signaling
The major types of signaling mechanisms that occur in multicellular organisms are paracrine, endocrine, autocrine, and direct signaling.
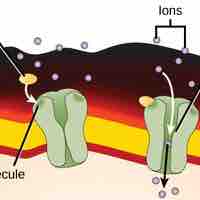
Types of Receptors
Receptors, either intracellular or cell-surface, bind to specific ligands, which activate numerous cellular processes.
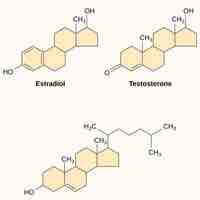
Signaling Molecules
Signaling molecules are necessary for the coordination of cellular responses by serving as ligands and binding to cell receptors.