Section 4
Zeroes of Polynomial Functions
Book
Version 13
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Algebra
Algebra
by Boundless
5 concepts
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
The fundamental theorem states that every non-constant single-variable polynomial with complex coefficients has at least one complex root.
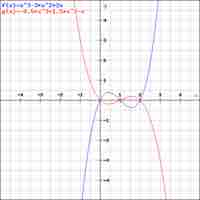
Finding Polynomials with Given Zeros
To construct a polynomial from given zeros, set
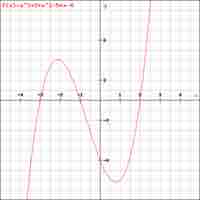
Finding Zeros of Factored Polynomials
The factored form of a polynomial reveals its zeros, which are defined as points where the function touches the
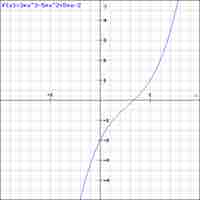
Integer Coefficients and the Rational Zeros Theorem
Each solution to a polynomial, expressed as
The Rule of Signs
The rule of signs gives an upper bound number of positive or negative roots of a polynomial.