Section 4
Additional Detail on Present and Future Values
By Boundless
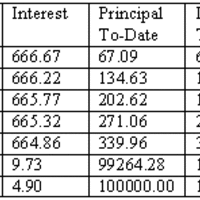
When borrowing money to be paid back via a number of installments over time, it is important to understand the time value of money and how to build an amortization schedule.
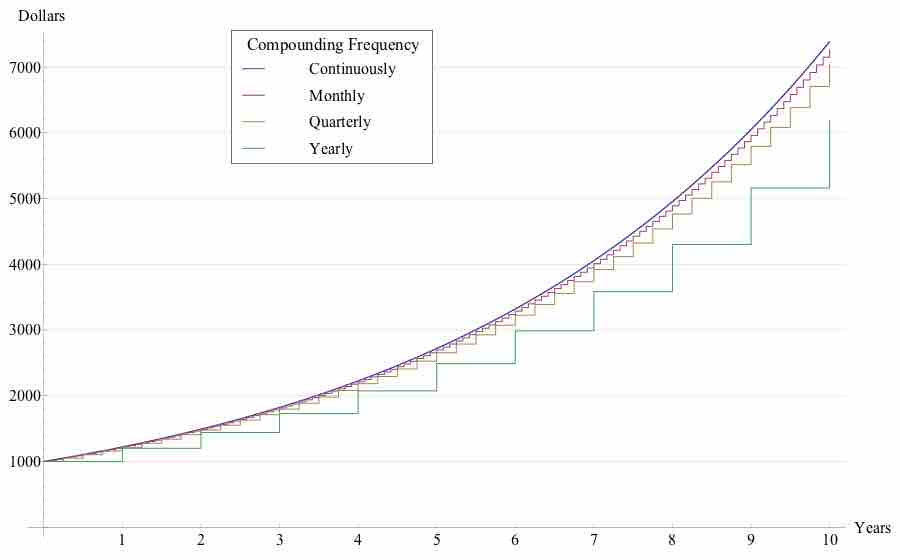
The value of money and the balance of the account may be different when considering fractional time periods.
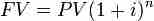
Present value (PV) and future value (FV) measure how much the value of money has changed over time.
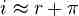
Variables, such as compounding, inflation, and the cost of capital must be considered before comparing interest rates.
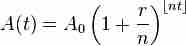
Finding the Effective Annual Rate (EAR) accounts for compounding during the year, and is easily adjusted to different period durations.
The present value of a perpetuity is simply the payment size divided by the interest rate and there is no future value.